The formula of hydroxide, represented as OH-, plays a crucial role in various chemical reactions and processes. Hydroxide ions are essential for understanding acid-base chemistry, environmental science, and even biological systems. In this article, we will delve deep into the nature of hydroxide, its significance, and applications, ensuring you have a thorough understanding of this important ion.
Whether you are a student, educator, or simply curious about chemistry, this guide will provide you with valuable insights into the properties and functionality of hydroxide. From its formation to its role in everyday life, we will cover all aspects of hydroxide in detail. Join us as we explore the fascinating world of hydroxide ions.
By the end of this article, you will not only understand the formula of hydroxide but also appreciate its importance in various fields such as chemistry, biology, and environmental science. Let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
- What is Hydroxide?
- The Chemical Formula of Hydroxide
- Properties of Hydroxide Ions
- How is Hydroxide Formed?
- Role of Hydroxide in Acid-Base Reactions
- Biological Significance of Hydroxide
- Hydroxide in Environmental Science
- Conclusion
What is Hydroxide?
Hydroxide is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula OH-. It consists of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom, carrying a negative charge. Hydroxide is commonly found in various compounds, particularly in bases.
Hydroxide ions play a fundamental role in chemical reactions, particularly in acid-base reactions, where they can act as a base by accepting protons (H+). Understanding hydroxide is critical for anyone studying chemistry or related fields.
The Chemical Formula of Hydroxide
The formula of hydroxide is succinctly represented as OH-. This notation indicates that the hydroxide ion has a net charge of -1. Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Oxygen (O): Atomic number 8, it is a vital element in many compounds.
- Hydrogen (H): Atomic number 1, it is the simplest and lightest element.
- Charge: The negative charge indicates that hydroxide is capable of forming ionic bonds with positively charged ions.
Properties of Hydroxide Ions
Hydroxide ions exhibit several notable properties:
- Basicity: Hydroxide ions are basic and can neutralize acids, forming water and salts.
- Solubility: Hydroxide salts are generally soluble in water, which contributes to their prevalence in aqueous solutions.
- Reactivity: Hydroxide ions can participate in various chemical reactions, including precipitation reactions and redox reactions.
Physical Properties
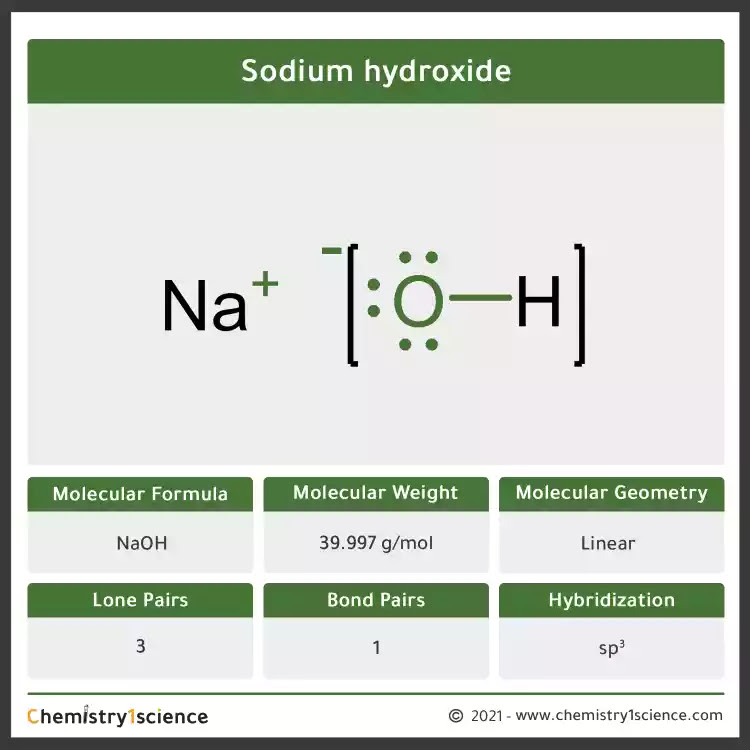
Hydroxide solutions, such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or potassium hydroxide (KOH), are caustic and can cause chemical burns. These solutions are clear and colorless and have a slippery feel due to their saponification reaction with fats.
Chemical Properties
Hydroxide ions can engage in the following reactions:
- Reacting with acids to form water and salt
- Forming metal hydroxides in reaction with metal ions
- Participating in hydrolysis reactions
How is Hydroxide Formed?
Hydroxide ions can be formed through various processes, including:
- Dissociation of Water: Water (H2O) can dissociate into hydroxide ions (OH-) and hydrogen ions (H+).
- Neutralization Reactions: When an acid reacts with a base, hydroxide ions can be produced.
- Electrolysis of Water: Passing an electric current through water can produce hydroxide ions at the cathode.
Role of Hydroxide in Acid-Base Reactions
In acid-base chemistry, hydroxide ions are crucial for understanding pH levels and neutralization reactions. When a base, such as sodium hydroxide, dissolves in water, it releases hydroxide ions, which increase the pH of the solution.
During a neutralization reaction, hydroxide ions react with hydrogen ions from an acid to form water:
H+ + OH- → H2O
This reaction is fundamental in both laboratory and industrial processes, illustrating the importance of hydroxide in chemical reactions.
Biological Significance of Hydroxide
Hydroxide ions play a vital role in biological systems. For instance, they are involved in:
- pH Regulation: Hydroxide ions help maintain the pH balance in biological fluids.
- Metabolic Reactions: Many enzymatic reactions involve hydroxide ions in their mechanisms, facilitating important biochemical processes.
- Cellular Respiration: Hydroxide ions are produced and consumed during cellular respiration and photosynthesis.
Hydroxide in Environmental Science
Hydroxide ions also have significant implications in environmental science. They are involved in:
- Water Treatment: Hydroxide is used to neutralize acids in wastewater treatment processes.
- Soil Chemistry: Hydroxide ions can affect soil pH, influencing nutrient availability for plants.
- Acid Rain Mitigation: Hydroxide ions can help neutralize acidic compounds in the atmosphere.
Conclusion
In summary, the formula of hydroxide (OH-) plays a pivotal role in various chemical, biological, and environmental processes. Understanding hydroxide is essential for students and professionals alike, as it contributes significantly to fundamental concepts in chemistry and beyond.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of hydroxide and its importance. If you have any questions or would like to share your thoughts, please leave a comment below. Don’t forget to share this article with others who might find it useful!
Thank you for reading, and we encourage you to explore more articles on our site for a deeper understanding of various scientific topics!
You Might Also Like
Noah Schnapp: The Rising Star Of HollywoodAlana Cho: The Rise Of A Modern Influencer
Ari Kytsya: The Rising Star Of Indonesian Entertainment
Happy Birthday Violin YouTube: Celebrate With Melodic Joy
Anna Ralphs: A Deep Dive Into Her Life And Career
Article Recommendations