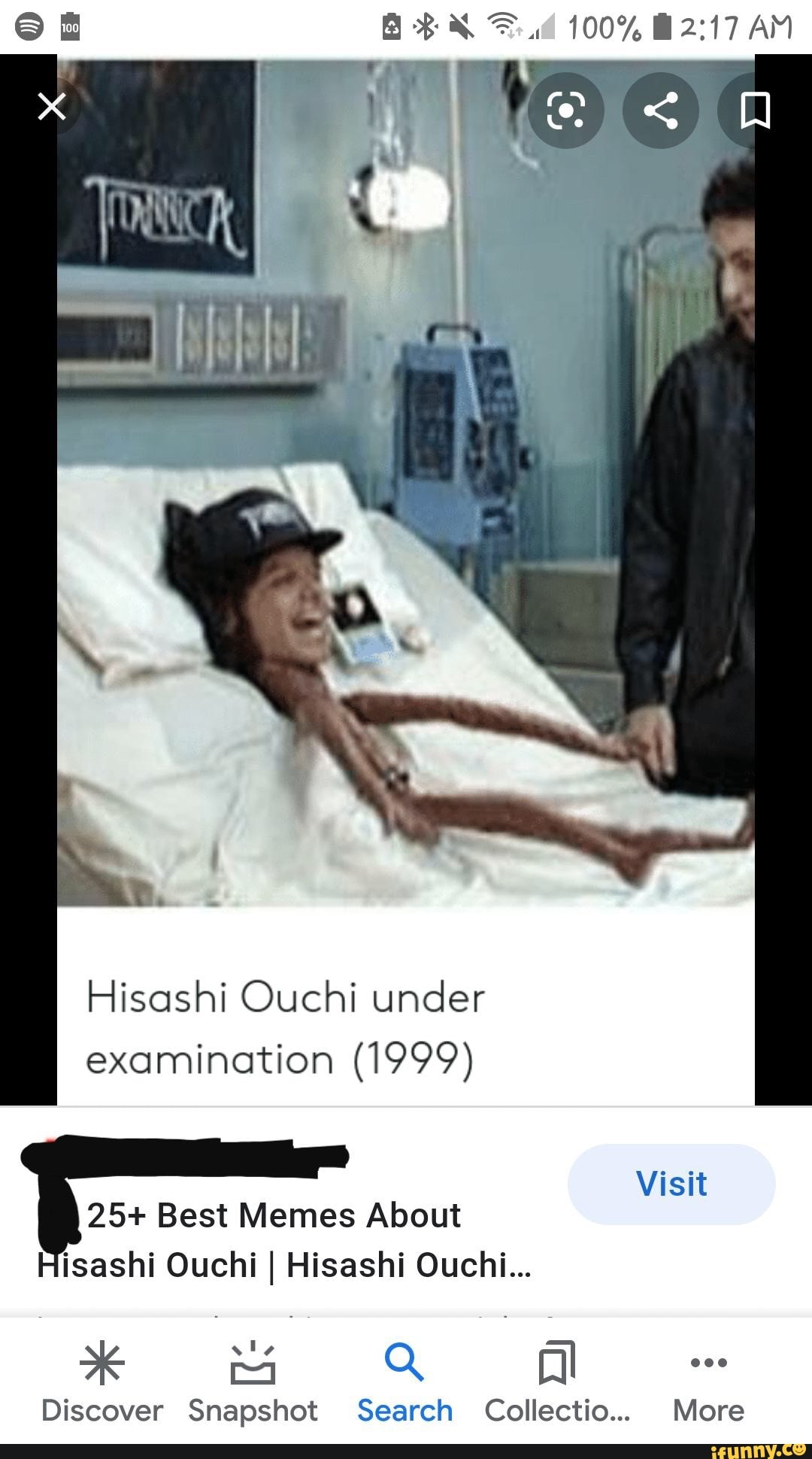
The story of Hisashi Ouchi is one that underscores the grave dangers of nuclear energy and the human cost of industrial accidents. As a young technician working at the Tokaimura nuclear facility in Japan, Ouchi became the victim of one of the most catastrophic nuclear incidents in history. This article will delve into the events surrounding the accident, the subsequent medical treatment he received, and the broader implications for safety in the nuclear industry.
In the early hours of September 30, 1999, a criticality accident took place at the Tokaimura plant, resulting in a massive release of radiation. Hisashi Ouchi, along with two other workers, was directly exposed to lethal doses of radiation. The incident not only claimed his life but also raised significant concerns about nuclear safety protocols and regulatory oversight in Japan and worldwide.
Through this in-depth exploration of Ouchi's life and the incident that marked it, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the risks associated with nuclear energy. We will also discuss the lessons that can be learned from this tragic event, emphasizing the need for stringent safety measures in the nuclear industry.
Table of Contents
- Biography of Hisashi Ouchi
- The Tokaimura Nuclear Accident
- Medical Treatment and Aftermath
- Impact on Nuclear Safety Regulations
- Public Reaction and Media Coverage
- Lessons Learned from the Incident
- Conclusion
- References
Biography of Hisashi Ouchi
Hisashi Ouchi was born on March 1, 1960, in Japan. He pursued a career in nuclear technology and became a skilled technician. His commitment to his work led him to the Tokaimura nuclear facility, where he played a crucial role in several nuclear operations.
| Personal Information | Details |
|---|---|
| Name | Hisashi Ouchi |
| Date of Birth | March 1, 1960 |
| Occupation | Nuclear Technician |
| Location | Tokaimura, Japan |
| Date of Incident | September 30, 1999 |
The Tokaimura Nuclear Accident
The Tokaimura accident occurred due to a series of critical errors made by workers at the facility. On that fateful day, Ouchi and his colleagues were involved in a process called "uranyl nitrate precipitation." The workers mistakenly mixed an excessive amount of uranium solution in a tank, which led to a criticality accident.
This criticality accident resulted in an uncontrolled nuclear fission reaction, releasing a significant amount of radiation into the facility. Hisashi Ouchi was one of the three workers who suffered the most severe radiation exposure, receiving a dose estimated at around 17 sieverts—far above the lethal limit for human beings.
The incident was a wake-up call for the nuclear industry, highlighting the importance of rigorous safety protocols and the need for better training for workers in high-risk environments.
Medical Treatment and Aftermath
Following the accident, Ouchi was rushed to the hospital, where he underwent extensive medical treatment. He experienced severe radiation sickness, which manifested as symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and hair loss. His treatment involved blood transfusions, medication to manage pain and infection, and other supportive care measures.
Despite the efforts of medical personnel, Ouchi's condition continued to deteriorate. He developed multiple organ failure, and his prognosis remained grim. After several months of suffering, Hisashi Ouchi tragically passed away on December 21, 1999, leaving behind a legacy that prompted a reevaluation of safety standards in the nuclear industry.
Impact on Nuclear Safety Regulations
The Tokaimura accident had far-reaching implications for nuclear safety regulations in Japan and beyond. In the wake of the incident, the Japanese government took several steps to enhance safety protocols, including:
- Reviewing and revising operational guidelines for nuclear facilities.
- Implementing stricter training requirements for personnel working in nuclear settings.
- Increasing oversight and inspections of nuclear facilities to ensure compliance with safety standards.
- Establishing a national safety commission to oversee nuclear operations.
These measures aimed to prevent future incidents and restore public trust in nuclear energy as a viable source of power. However, public sentiment remained wary of nuclear energy, leading to intensified debates about its safety and sustainability.
Public Reaction and Media Coverage
In the aftermath of the Tokaimura accident, public reaction was overwhelmingly negative. Many people expressed their fears about the risks associated with nuclear energy, and protests against nuclear facilities gained momentum across Japan.
The media extensively covered Ouchi's tragic story, bringing awareness to the dangers of radiation exposure and the importance of safety in nuclear operations. Documentaries, articles, and news segments explored the incident in detail, ensuring that the memory of Hisashi Ouchi and the lessons learned from his suffering would not be forgotten.
Lessons Learned from the Incident
The Tokaimura nuclear accident serves as a stark reminder of the potential consequences of negligence in high-risk industries. Key lessons learned include:
- The critical importance of adhering to safety protocols and regulations.
- The need for ongoing training and education for workers in nuclear facilities.
- The necessity of a robust emergency response plan to address accidents when they occur.
- The value of transparency in communicating risks and safety measures to the public.
These lessons continue to resonate within the nuclear industry, influencing policies and practices aimed at improving safety and preventing future tragedies.
Conclusion
Hisashi Ouchi's story is a tragic yet important part of the narrative surrounding nuclear energy. The Tokaimura accident not only claimed his life but also highlighted significant flaws in safety protocols and regulatory oversight. This incident serves as a critical reminder of the need for continuous improvement in safety measures within the nuclear industry.
As we reflect on the lessons learned from this tragedy, it is essential to advocate for stronger safety standards and ensure that the sacrifices made by individuals like Ouchi are not in vain. We encourage readers to engage in discussions about nuclear safety and consider the implications of energy choices on public health and safety.
References
1. "The Tokaimura Nuclear Accident." Nuclear Regulatory Authority of Japan.
2. "Radiation Exposure and Health Effects." World Health Organization.
3. "Lessons from the Tokaimura Accident." International Atomic Energy Agency.
You Might Also Like
What Happened To Lisa Weiss: Unraveling The MysteryExploring The Phenomenon Of Yes King Original Video: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding And Utilizing Icebreaker Techniques From Page 136 Of The Icebreaker Book
Tim Scott's Daughter: A Closer Look At Her Life And Influence
5StarsStocks.com Value Stocks: Unlocking The Potential Of Value Investing
Article Recommendations